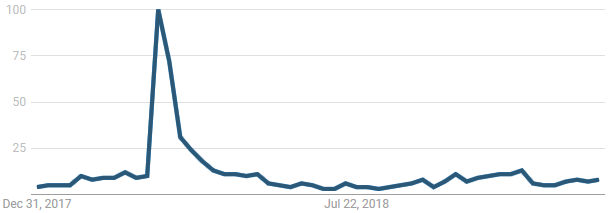
2018 was a big year for information security and data privacy. The European General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”) became effective and helped bring greater awareness to the handling of personal data while several U.S. states passed or amended their privacy laws. Below we have compiled a list of the most significant privacy and security developments of 2018.
1) GDPR

GDPR had a big impact in 2018 and brought greater awareness to the handling of personal data. We expect its impact to continue to grow in 2019 when some of the larger investigations are expected to begin.
2) Carpenter v. United States

In a 5-4 decision written by Chief Justice Roberts – and invoking the types of government oppression on liberty that led to the American Revolution — the Supreme Court reversed the Court of Appeal’s decision and held that the government must obtain a warrant to search a target’s Cell-Site Location Information (“CSLI”). The Court found that customers have a reasonable expectation of privacy in CSLI based on the sweeping extent of location information collected, the automatic nature by which wireless carriers collect the information, the inferences that can be made about a person’s movements from such data, and the extent to which government could obtain information collected retroactively on hundreds of millions of phone users.
3) CCPA

Following the California Consumer Privacy Act’s (“CCPA”) hasty enactment in June 2018, there was broad agreement among industry groups, privacy advocates, and state government officials that the law needed to be amended to fix a number of drafting errors, such as erroneous cross-references and sentence fragments. On September 23, 2018, the law was amended as SB 1121. While the amendments did not change the CCPA’s core compliance requirements, they do include some significant clarifications to the law, as well as technical corrections. We expect to see more clarifications/revisions in 2019.
4) Ohio Safe Harbor

Ohio became the first state to enact legislation providing liability protection for businesses that implement a written cybersecurity program that “reasonably conforms” to certain cybersecurity frameworks or laws to protect personal information. This approach is in stark contrast to that taken by California in its Consumer Privacy Act, which established a private right of action against organizations that fail to maintain reasonable security measures under California law.
5) CLOUD Act

The CLOUD Act was enacted, effectively mooting the closely watched United States v. Microsoft case and marking a watershed moment in federal and international surveillance law. The Act codifies mechanisms for both U.S. and foreign governments to enforce surveillance orders on data located outside of their territorial boundaries, with major consequences for providers of electronic communications and remote computing services who have operations in the United States.